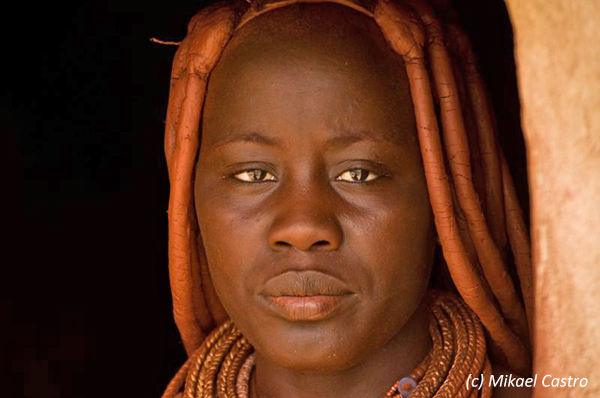Himba
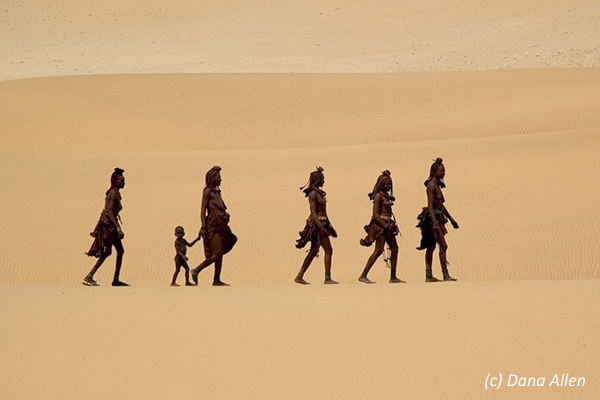
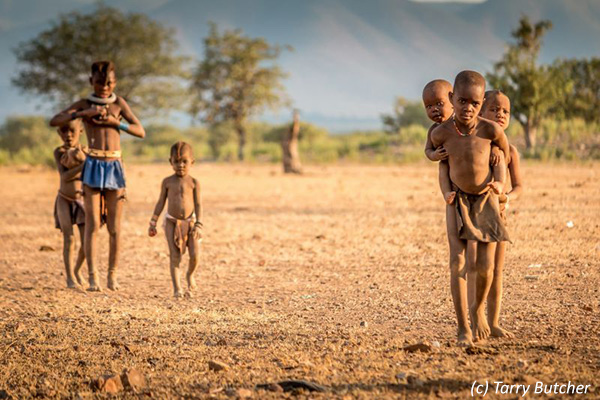
The Himba, Tjimba and other Herero people who inhabit Namibia’s remote north-western Kunene Region are loosely referred to as the Kaokovelders. The largest group of Kaokovelders is the Himba, semi-nomads who live in scattered settlements throughout the Kunene Region. They are a tall, slender and statuesque people, characterized especially by their proud yet friendly bearing. The women especially are noted for their unusual sculptural beauty, enhanced by intricate hairstyles and traditional adornments. They rub their bodies with red ochre and fat, a treatment that protects their skins against the harsh desert climate.
The homes of the Himba of Kaokoland are simple, cone-shaped structures of saplings, bound together with palm leaves and plastered with mud and dung. The men build the structures, while the women mix the clay and do the plastering. A fire burns in the headman’s hut day and night, to keep away insects and provide light and heating.
A family may move from one home to another several times a year to seek grazing for their goats and cattle. Men, women and children wear body adornments made from iron and shell beads. A Himba woman spends as much as three hours a day on her appearance. First she bathes, then she anoints herself with her own individually prepared mixture that not only protects her skin from the harsh desert sun and keeps insects away. She uses another mixture of butter fat, fresh herbs and black coals to rub on her hair, to keep it from falling out, and she ‘steams’ her clothes regularly over the permanent fire. Men, women and children adorn themselves with necklaces, bracelets, anklets and belts made from iron and shell beads. With their unusual and striking designs, these items have gained a commercial value and are being produced on a small scale for the urban market. Sculptural headrests, in particular, are sought after items.